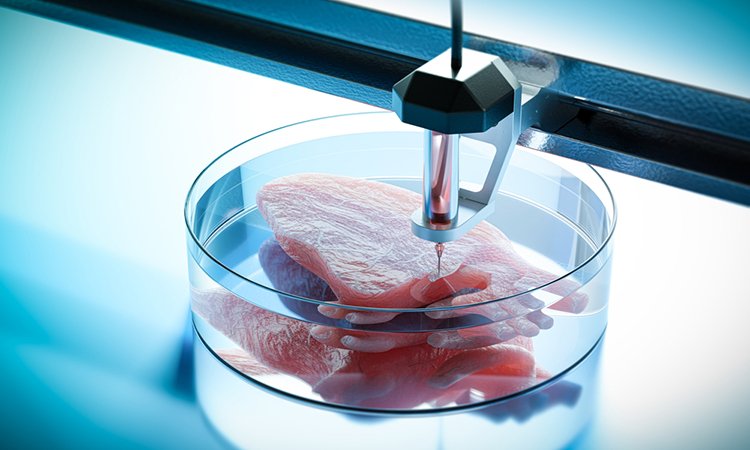
Have you ever imagined a world where damaged organs can be replaced with ones grown in a lab? Bioprinting technology is rapidly turning this science fiction into a reality. This blog post will delve into the fascinating world of bioprinting, exploring its mechanism, how it works, and the machines that make it possible.
The Bioprinting Blueprint: Cells, Bioinks, and Layered Creation
At its core, bioprinting is a form of 3D printing specifically designed for biological materials. Instead of plastic or metal filaments, bioprinters use bioinks – a combination of living cells and a supportive scaffolding material. These bioinks are carefully formulated to provide the necessary nutrients and structure for the cells to survive and thrive.
The bioprinting process itself is similar to traditional 3D printing. A digital design (think a blueprint for your tissue) is fed into the printer. The bioprinter then translates this design into instructions, depositing the bioink layer-by-layer to create the desired 3D structure. This allows for precise control over the placement of cells, mimicking the natural organization of tissues.
Bioprinting in Action: From Research to Regeneration
Bioprinting holds immense potential for various applications. Here are a few exciting areas where this technology is making waves:
- Tissue Engineering: Bioprinted tissues can be used to study diseases, test new drugs, and potentially even create transplantable organs. Imagine a future where patients no longer have to wait on organ donor lists!
- Drug Discovery: Bioprinted tissues can provide a more realistic environment to test the effects of new drugs compared to traditional petri dish methods. This could lead to faster and more effective drug development.
- Personalized Medicine: Bioprinting could allow for the creation of tissues specific to a patient’s own cells, paving the way for personalized treatments and therapies.
The Machines Behind the Magic: Bioprinting Technologies
Several bioprinting techniques are being developed, each with its own advantages and limitations. Here’s a peek into two common methods:
- Extrusion Bioprinting: This method uses a pressurized system to deposit bioink through a nozzle, similar to a hot glue gun. It’s a popular choice due to its simplicity and versatility.
- Inkjet Bioprinting: This technique works similarly to an inkjet printer, propelling droplets of bioink with high precision. It allows for highly detailed structures but may not be suitable for all cell types.
As bioprinting technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated machines and techniques to emerge.
The Future of Bioprinting: Printing a Healthier Tomorrow
Bioprinting is a rapidly growing field with the potential to revolutionize medicine. While there are still challenges to overcome, such as vascularization (supplying blood flow) for complex organs, the future looks bright. Bioprinting has the potential to address organ shortages, personalize treatments, and accelerate medical discoveries. This technology is bringing us closer to a future where regeneration and repair are not science fiction, but a reality.