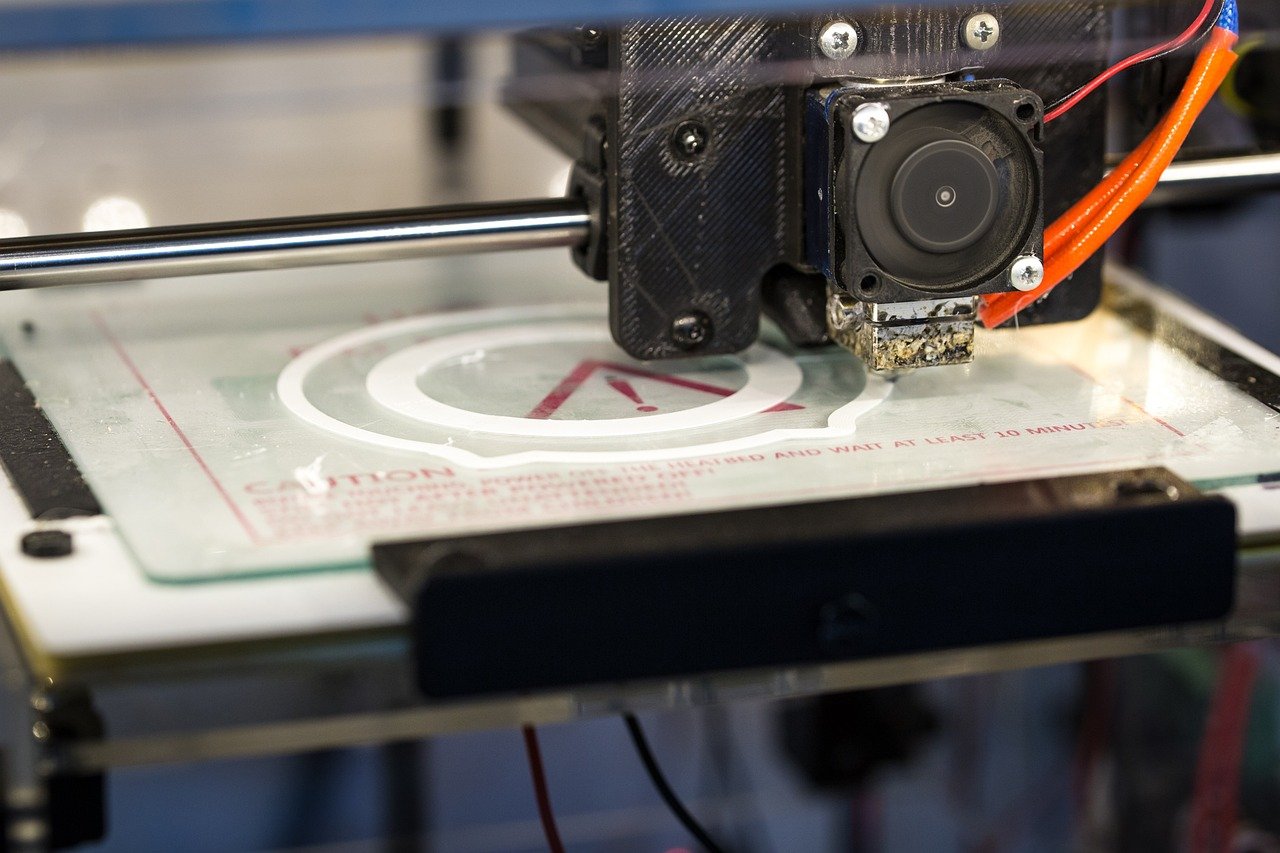
The ability to transform digital dreams into tangible objects has long been the stuff of science fiction. But with 3D printing technology, this fantastical concept has become a reality. This blog will delve into the fascinating world of 3D printers, exploring their mechanism, working process, and the machines that bring 3D designs to life.
Building Block by Block: The Mechanism of 3D Printing
At its core, 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing (think carving a sculpture), 3D printers build objects layer by layer. This process relies on three key components:
- Digital Design: The first step involves creating a 3D model using computer-aided design (CAD) software or obtaining a model online. This digital file serves as the blueprint for the object to be printed.
- Slicing Software: This software slices the 3D model into hundreds or even thousands of thin horizontal layers. Each layer represents a single cross-section of the object.
- 3D Printer: The heart of the operation, the 3D printer reads the sliced model and precisely deposits material layer-by-layer to physically create the object.
The Magic of Materialization: How 3D Printing Works
There are several 3D printing techniques, each using different materials and processes. Here’s a breakdown of two popular methods:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common method, often used in home 3D printers. It works by feeding a filament of plastic (PLA or ABS are common) through a heated nozzle. The nozzle melts the plastic and deposits it layer-by-layer, following the sliced model instructions. The material cools and solidifies, building the object one layer at a time.
- Stereolithography (SLA): This technique uses a vat of liquid resin and a laser beam to cure the resin layer-by-layer. The laser selectively hardens the resin based on the sliced model, forming the desired object with high precision and smooth surface finish.
The Machines that Make It Happen: Different Types of 3D Printers
3D printers come in various shapes and sizes, catering to different needs and budgets. Here are a few examples:
- FDM Printers: These are generally the most affordable and user-friendly option, making them ideal for hobbyists and home use.
- Resin Printers: Offering higher resolution and smoother finishes, resin printers are popular for creating detailed prototypes and models.
- Metal Printers: Utilizing metal powder and lasers, these high-end machines can create functional metal parts for industrial applications.
The Future of 3D Printing: A World of Possibilities
3D printing technology is rapidly evolving, and its applications are vast. From creating custom prosthetics to printing entire houses, the possibilities are seemingly endless. Here are some exciting areas where 3D printing is making waves:
- Prototyping: 3D printing allows for quick and affordable creation of prototypes, speeding up the design and development process.
- Manufacturing: Complex parts and customized products can be produced on-demand with 3D printing, reducing reliance on traditional manufacturing methods.
- Healthcare: 3D printing is being used to create customized implants, prosthetics, and even bioprinted tissues for medical applications.
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge, transforming the way we design, create, and interact with the world around us.